diabetic ketoacidosis workup|Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): Practice Essentials, Background : Cebu Diabetic ketoacidosis is characterized by a serum glucose level greater than 250 mg per dL, a pH less than 7.3, a serum bicarbonate level less than 18 mEq per L, . PRBS PNP | PNP RETIREMENT & BENEFITS ADMINISTRATION SERVICE
PH0 · Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state
PH1 · Diabetic ketoacidosis
PH2 · Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Evaluation and Treatment
PH3 · Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): Practice Essentials, Background
PH4 · Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Workup: Approach Considerations, P
PH5 · Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Workup
PH6 · Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
PH7 · Diabetic Ketoacidosis
PH8 · Adult Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Playing slots in downtown Las Vegas egad this video at El Cortez Casino! Let’s play some classics and new slot machine games!!If you watch my videos much I’m.
diabetic ketoacidosis workup*******Diabetic ketoacidosis is typically characterized by hyperglycemia of over 250 mg/dL, a bicarbonate level of less than 18 mEq/L, and a of pH less than 7.30, with ketonemia and ketonuria.Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is an acute, major, life-threatening complication of . It is a life-threatening complication of diabetes and typically seen in patients with type-1 diabetes mellitus, though it may .
Diabetic ketoacidosis is characterized by a serum glucose level greater than 250 mg per dL, a pH less than 7.3, a serum bicarbonate level less than 18 mEq per L, .Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is characterised by a biochemical triad of hyperglycaemia, ketonaemia, and acidaemia, with rapid symptom onset. Common symptoms and signs . Insulin reverses diabetic ketoacidosis. In addition to fluids and electrolytes, insulin is given, usually through a vein. A return to regular insulin therapy may be . Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is an acute, major, life-threatening complication of diabetes that mainly occurs in patients with type 1 diabetes, but it is not . DKA management checklist. diagnostic evaluation ( more) Minimum evaluation for a patient with DKA: Electrolytes including Ca/Mg/Phos, complete blood count with differential, urinalysis, EKG, . Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS, also known as hyperosmotic hyperglycemic nonketotic state [HHNK]) are two of the .Pathophysiology. Defining features include hyperglycemia (glucose > 200mg/dl), acidosis (pH < 7.3), and ketonemia. Hyperglycemia. Leads to osmotic diuresis and depletion of electrolytes including sodium, .
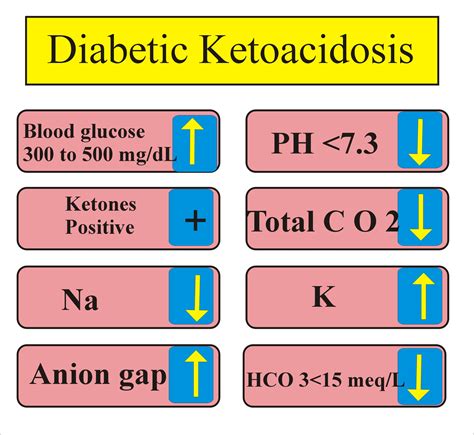
DEFINITION. A metabolic acidosis characterized by the triad of hyperglycemia (glucose >250 mg/dL), metabolic acidosis (arterial pH ≤ 7.3, serum .diabetic ketoacidosis workup diagnostic evaluation ( more) Minimum evaluation for a patient with DKA: Electrolytes including Ca/Mg/Phos, complete blood count with differential, urinalysis, EKG, pregnancy test as appropriate. . You have many symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis. These include excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea and vomiting, stomach pain, weakness or fatigue, shortness of breath, fruity-scented breath, and confusion. Remember, untreated diabetic ketoacidosis can lead to death. Request an appointment.
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is an acute, major, life-threatening complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, ketoacidosis, and ketonuria.It occurs when absolute or relative insulin deficiency inhibits the ability of glucose to enter cells for utilization as metabolic fuel, the result being that the liver rapidly breaks down .
Ketoacidosis is a metabolic state associated with pathologically high serum and urine concentrations of ketone bodies, namely acetone, acetoacetate, and beta-hydroxybutyrate. During catabolic states, fatty acids are metabolized to ketone bodies, which can be readily utilized for fuel by individual cells in the body. Of the three major .
Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in adults: Treatment; Etiology and diagnosis of distal (type 1) and proximal (type 2) renal tubular acidosis; Etiology, diagnosis, and treatment of hypoaldosteronism (type 4 RTA) Fasting ketosis and alcoholic ketoacidosis; Inhalant misuse in children and adolescents

DDxOf: Management of DIabetic Ketoacidosis; References. ↑ Lebovitz HE: Diabetic ketoacidosis. Lancet 1995; 345: 767-772. ↑ Nagler J et al. Capnography: A valuable tool for airway management. Emerg Med Clin North Am, 26(4):881, Nov 2008. ↑ Peters AL et al. Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Potential Complication of Treatment With Sodium . The diagnosis of NAGMA may be made in one of two ways: (red arrows above)Patient has normal anion gap with metabolic acidosis (bicarbonate < 22 mM). Patient has an anion gap metabolic acidosis, but the decrease in bicarbonate is much greater than the elevation in anion gap (indicating the combination of an anion-gap metabolic .Clinical Features. Frequency of signs and symptoms among 37 pediatric patients with diabetic ketoacidosis in Nigeria. May be the initial presenting of an unrecognized Type-1 diabetes mellitus patient. Signs/symptoms may include: Tachypnea, Kussmaul's breathing. Polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, poor weight gain /weight loss. Signs of dehydration.Aim to keep the BGL between 5-10 mmol/L. If BGL falls below 5mmol/L or is falling rapidly (>5 mmol/L/hour) in the range between 5-15 mmol/L and the child remains acidotic, increase the glucose content to 10%. Insulin infusion rate should only be decreased if BGL continues to fall despite glucose concentration of 10%. Acute toxic-metabolic encephalopathy (TME), which encompasses delirium and the acute confusional state, is an acute condition of global cerebral dysfunction in the absence of primary structural brain disease [ 1 ]. An overview of TME in hospitalized patients will be discussed here; a diagnostic approach to delirium is presented separately.We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.May be the initial presenting of an unrecognized Type-1 diabetes mellitus patient. Presenting signs/symptoms include altered mental status, tachypnea, abdominal pain. Perform a thorough neurologic exam (cerebral edema increases mortality significantly, especially in children) Assess for possible inciting cause (esp for ongoing infection; see . Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS, also known as hyperosmotic hyperglycemic nonketotic state [HHNK]) are two of the most serious acute complications of diabetes. They are part of the spectrum of hyperglycemia, and each represents an extreme in the spectrum. In addition, ketoacidosis with mild .diabetic ketoacidosis workup Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): Practice Essentials, Background Practice Essentials. In 1940, Dillon and colleagues first described alcoholic ketoacidosis (AKA) as a distinct syndrome. AKA is characterized by metabolic acidosis with an elevated anion gap, elevated serum ketone levels, and a normal or low glucose concentration. [ 1, 2, 3] The diagnosis of AKA requires arterial blood gas (ABG) . Update 2023: A prospective single center study including 177 adult patients with mild to moderate DKA found a significant reduction in median ED length of stay (-3.0, 95%CI -8.5 to -1.4) in patients who were treated with subcutaneous insulin during the study period as part of the SQuID (subcutaneous insulin in diabetic ketoacidosis) protocol . Introduction. In 2009, there were 140,000 hospitalizations for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) with an average length of stay of 3.4 days. 1 The direct and indirect annual cost of DKA hospitalizations is 2.4 billion US dollars. Omission of insulin is the most common precipitant of DKA. 2, 3 Infections, acute medical illnesses involving the . Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA, EDKA) is a clinical syndrome occurring both in type 1 (T1DM) and type 2 (T2DM) diabetes mellitus characterized by euglycemia (blood glucose less than 250 mg/dL) in the presence of severe metabolic acidosis (arterial pH less than 7.3, serum bicarbonate less than 18 mEq/L) and . Alcoholic ketoacidosis (AKA) is a clinical syndrome seen mostly in patients with chronic alcohol use disorder and frequently seen in patients who binge drink. Typical patients are usually chronic drinkers who are unable to tolerate oral nutrition for a 1 to 3 day period. Patients often have a recent bout of heavy drinking before the period of relative .
Contextual translation of "nakakawala" into English. Human translations with examples: nakakawala, nakakawalang gana, nakakawala ng pagod.
diabetic ketoacidosis workup|Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): Practice Essentials, Background